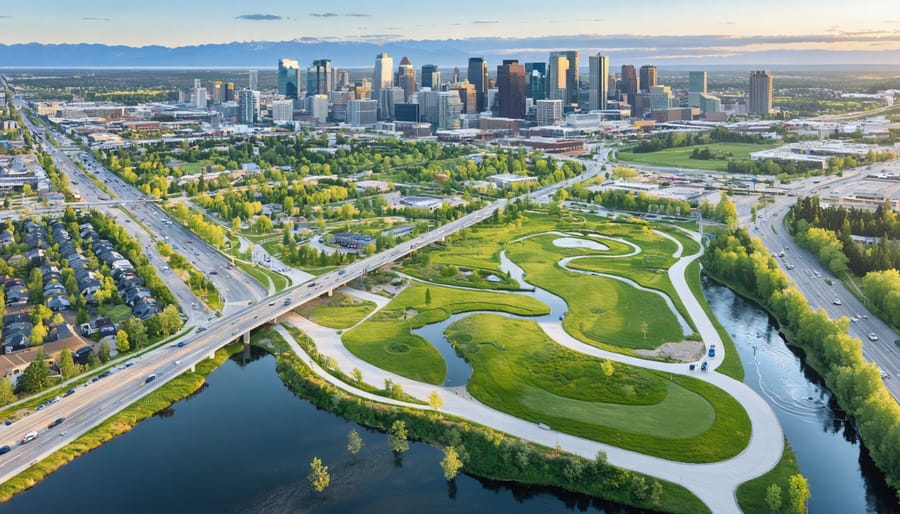
Water shapes the future of our cities, demanding innovative approaches to urban water management that balance population growth with environmental stewardship. Across Canadian municipalities, from Calgary to Vancouver, integrated water management plans have become essential tools for securing sustainable water resources while protecting vital ecosystems. These comprehensive strategies address everything from stormwater capture and groundwater preservation to drought resilience and flood prevention, working in harmony with natural water cycles.
Modern urban water management extends far beyond traditional infrastructure, embracing green solutions like bioswales, permeable surfaces, and constructed wetlands. These nature-based approaches not only manage water more effectively but also create vibrant community spaces, enhance biodiversity, and improve urban livability. For Canadian cities facing increasing climate pressures, well-designed water management plans offer a blueprint for resilient, sustainable communities.
Municipal leaders and environmental professionals now recognize that successful water management requires collaboration between multiple stakeholders – from city planners and engineers to environmental scientists and community members. By integrating traditional knowledge with cutting-edge technology and environmental best practices, cities can develop robust water management strategies that serve both current needs and future generations while preserving our precious water resources.

Building Sustainable Water Systems for Alberta’s Future
Water Conservation Strategies That Work
In Alberta’s urban centers, implementing effective water conservation strategies has become increasingly crucial for sustainable development. Successful approaches include the installation of smart meters and leak detection systems, which have helped municipalities reduce water loss by up to 30%. The City of Calgary’s retrofit program for older buildings has demonstrated particular success, achieving water savings of 40-50% in participating structures.
Low-flow fixtures and appliances represent another practical solution, with modern toilets using just 4.8 litres per flush compared to older models that consumed up to 13 litres. Edmonton’s rebate program for water-efficient appliances has encouraged over 15,000 households to make the switch, resulting in significant water savings.
Rainwater harvesting systems have gained traction, with collection tanks ranging from 200 to 5,000 litres becoming common in new developments. These systems can reduce potable water demand by up to 40% for landscape irrigation and non-potable indoor uses.
Public education campaigns have proven equally valuable. The “Every Drop Counts” initiative in Lethbridge achieved a 15% reduction in residential water use through simple behavioral changes. Community-based programs focusing on xeriscaping and drought-resistant landscaping have shown particular success in reducing outdoor water consumption by up to 50%.
Real-time monitoring and automated irrigation systems have revolutionized urban landscape management. Parks and public spaces using these systems report water savings of 25-35% while maintaining green spaces that enhance community well-being.
Infrastructure Innovation
Modern urban water infrastructure is undergoing a remarkable transformation across Canadian municipalities, with innovations focusing on efficiency and sustainability. The integration of smart water management systems has revolutionized how we monitor and control water distribution, reducing waste by up to 30% in pilot projects across Alberta.
Advanced leak detection technology now uses acoustic sensors and artificial intelligence to identify potential problems before they become major issues. These systems can pinpoint leaks within metres, allowing maintenance teams to respond quickly and efficiently. In Calgary, this approach has already saved millions of litres of water annually.
Green infrastructure solutions are gaining traction, with permeable pavements and bioswales becoming standard features in new developments. These natural systems help manage stormwater while replenishing groundwater supplies. Rain gardens and constructed wetlands are being integrated into urban landscapes, providing both water management benefits and creating valuable wildlife habitats.
Underground water storage facilities are being modernized with real-time monitoring capabilities. These improvements allow operators to better manage water levels during peak demand periods and extreme weather events. Several communities in southern Alberta have implemented these systems, resulting in more reliable water supply during dry seasons.
Municipalities are also investing in water recycling facilities that use advanced filtration and treatment processes. These systems can process grey water for non-potable uses like irrigation and industrial applications, reducing the strain on drinking water supplies. The technology has proven particularly valuable for agricultural operations near urban centres, where treated water can support crop irrigation while maintaining high safety standards.

Environmental Impact Assessment
Water Quality Protection
Maintaining high water quality standards in urban areas requires a comprehensive approach that starts with water source protection and extends throughout the distribution system. In Alberta’s urban centres, we’ve seen remarkable success with integrated watershed management strategies that combine natural filtration systems with modern treatment technologies.
Key measures include establishing vegetative buffer zones along waterways, implementing strict stormwater management protocols, and regular monitoring of water quality parameters. Many municipalities have adopted green infrastructure solutions, such as bioswales and rain gardens, which naturally filter pollutants before they reach our water sources.
Regular testing programs track essential indicators like turbidity, pH levels, and bacterial content, ensuring our drinking water meets or exceeds federal guidelines. Communities across Alberta have successfully implemented watershed protection programs that engage local farmers in reducing agricultural runoff through improved irrigation practices and proper chemical application timing.
Treatment facilities employ multiple barriers of protection, including advanced filtration systems and UV disinfection. These systems work together with natural watershed protection measures to ensure consistent water quality. Recent innovations in real-time monitoring technology have allowed treatment plants to respond quickly to any quality concerns, maintaining safe drinking water for our communities.
Remember, protecting our water quality is a shared responsibility that benefits both urban and rural residents, supporting sustainable growth while preserving our natural resources for future generations.
Success Stories: Canadian Cities Leading the Way
Several Canadian cities have emerged as pioneers in urban water management, offering valuable lessons for communities across the country. Edmonton stands out with its award-winning EPCOR SIRP (Stormwater Integrated Resource Plan), which has successfully reduced flood risks while creating multi-purpose green spaces. The city’s naturalized stormwater management facilities not only handle excess water but also provide recreational areas and wildlife habitats, demonstrating how water management can enhance community life.
In Halifax, the innovative Halifax Water’s Integrated Resource Plan has become a model for coastal cities. Their approach combines traditional infrastructure with natural solutions, including the restoration of wetlands along the Bedford Basin. This integrated strategy has reduced water treatment costs by 15% while improving water quality in the harbour.
Vancouver’s Rain City Strategy showcases how urban planning can embrace rainfall as a resource rather than a nuisance. The city has implemented over 250 green infrastructure projects, including rain gardens and permeable pavements, managing 90% of annual rainfall through natural processes. Local businesses report reduced flooding incidents, and neighbourhood satisfaction has increased significantly.
Calgary’s Watershed+ program deserves special mention for its unique approach to combining water management with public art and community engagement. The program has transformed traditional stormwater ponds into beautiful public spaces while maintaining their functional capability. The Centre Street watershed project, for example, handles major storm events while providing year-round recreational opportunities.
These success stories share common elements: strong community involvement, integration of green infrastructure with existing systems, and careful consideration of local conditions. They demonstrate that effective urban water management not only addresses technical challenges but also creates lasting benefits for residents, wildlife, and the environment. The documented success of these initiatives provides valuable blueprints for other Canadian municipalities looking to enhance their water management strategies.
Practical Implementation Steps
To implement an effective urban water management plan, municipalities should start by conducting a comprehensive water audit to establish baseline usage patterns. Begin with installing smart meters throughout the distribution system to monitor real-time water flow and identify potential leaks or inefficiencies.
Create a stakeholder engagement strategy by forming a water management committee that includes local farmers, business owners, and community representatives. This collaborative approach ensures diverse perspectives are considered when developing conservation initiatives.
Develop a three-tier implementation timeline: immediate actions (0-6 months), short-term goals (6-18 months), and long-term objectives (18+ months). Prioritize infrastructure upgrades based on assessment results, focusing first on high-risk areas or those with significant water loss.
Establish water conservation bylaws that encourage responsible usage while implementing incentive programs for properties that adopt water-efficient technologies. Consider offering rebates for low-flow fixtures or xeriscaping projects.
Set up a monitoring and reporting system to track progress and adjust strategies as needed. Regular community updates through newsletters and town halls help maintain transparency and engagement throughout the implementation process.
Remember to allocate adequate funding and resources for ongoing maintenance and emergency response capabilities to ensure the plan’s long-term success.
Urban water management plans are vital tools for building resilient and sustainable communities across Alberta and beyond. By implementing these comprehensive strategies, we can protect our precious water resources while supporting both agricultural needs and urban development. The success of these plans depends on active participation from all stakeholders, from farmers to city planners. We encourage you to get involved with your local water management initiatives, attend community planning sessions, and share your agricultural expertise. Remember, every step we take toward better water management helps secure our future water supply and supports sustainable farming practices. Together, we can create effective solutions that benefit both our agricultural communities and urban centres while preserving this essential resource for generations to come.