Harvest rainwater from your roof to boost your farm’s resilience and embrace sustainable agriculture practices. Install gutters and downspouts to channel water into storage tanks. Regularly clean and maintain your roof, gutters, and tanks to ensure water quality. Use the collected rainwater for irrigation, livestock, and cleaning equipment to conserve groundwater and reduce costs.
Assessing Your Roof’s Rainwater Potential
Calculating Potential Rainwater Yield
To calculate the potential rainwater yield from your roof, you can use a simple formula that considers the roof area, average rainfall, and a conversion factor. First, determine your roof’s surface area in square meters. Then, multiply this value by the average rainfall in Alberta, which is approximately 365 mm per year (0.365 m). Finally, multiply the result by a conversion factor of 0.90 to account for minor losses due to evaporation or overflow.
Here’s the formula:
Potential Rainwater Yield (L) = Roof Area (m²) × Average Rainfall (m) × 0.90 × 1000
For example, if your barn has a roof area of 200 m² and your region receives the average rainfall, the potential rainwater yield would be:
200 m² × 0.365 m × 0.90 × 1000 = 65,700 L per year
That’s enough to fill over 260 large rain barrels! Even a smaller house with a 100 m² roof could collect about 32,850 L annually. By plugging in your roof measurements and local rainfall data, you can quickly estimate how much rainwater you could be harvesting for your farm or garden.
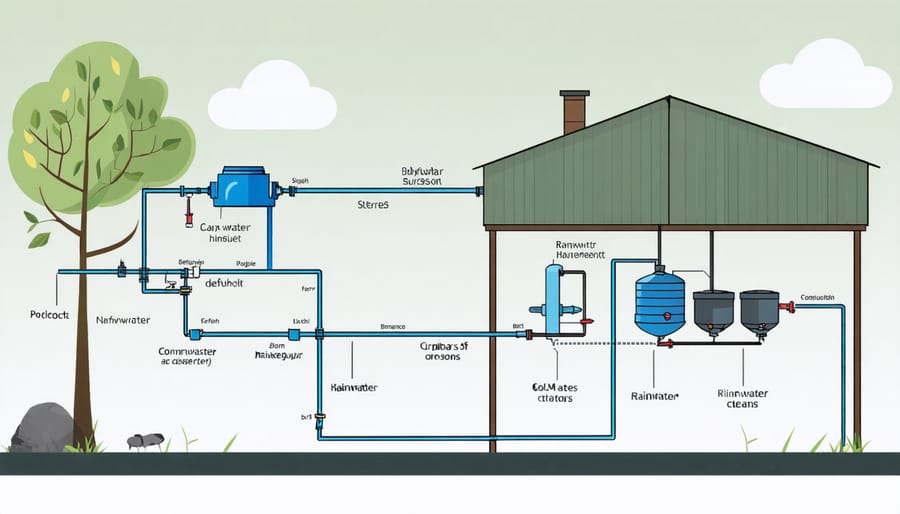
Setting Up Your Rainwater Harvesting System
Gutter and Downspout Preparation
To ensure optimal water collection from your roof, it’s essential to properly prepare your gutters and downspouts. Begin by thoroughly cleaning your gutters, removing any debris such as leaves, twigs, and sediment that may obstruct water flow. Check for leaks, cracks, or damage, and repair or replace sections as needed to prevent water loss. Ensure your gutters are securely fastened and properly sloped towards the downspouts for efficient drainage.
Next, inspect your downspouts and clear any blockages. Consider installing gutter guards to minimize future debris accumulation. Adjust the downspouts to direct water away from your home’s foundation and towards your rainwater storage system. Depending on your setup, you may need to extend the downspouts or use flexible piping to reach your storage tanks.
Before connecting your downspouts to the storage system, familiarize yourself with the legalities of rainwater harvesting in your area. Some regions may have specific regulations or requirements for rainwater collection. Once you’ve confirmed compliance, securely attach the downspouts to your storage tanks using appropriate fittings and seals to prevent leaks and ensure efficient water transfer.
Regular maintenance of your gutters and downspouts is crucial for optimal rainwater harvesting. Periodically clean and inspect the system, especially before and after heavy rainfall events, to ensure it remains in good working condition. By properly preparing and maintaining your gutters and downspouts, you’ll maximize the amount of clean rainwater collected for your agricultural needs.

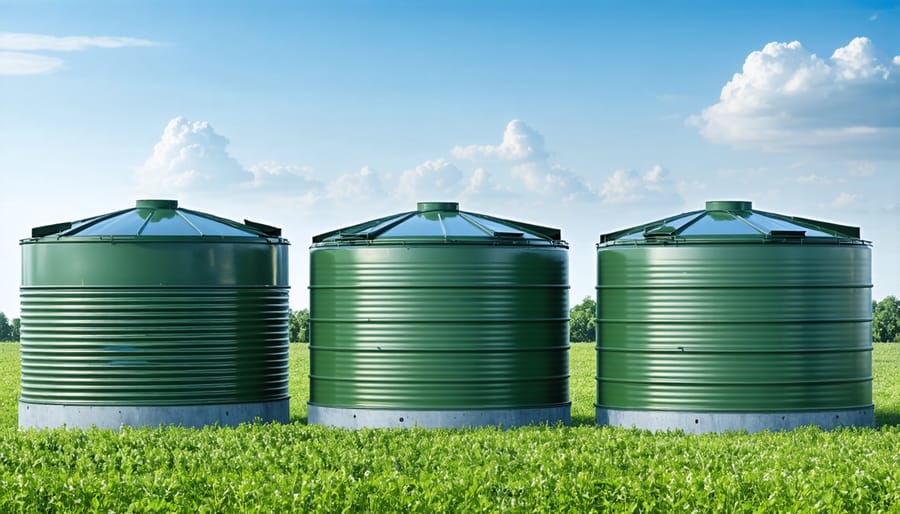
Choosing the Right Storage Tank
When selecting a storage tank for your harvested rainwater, consider the material, size, and location. Common materials include polyethylene, fiberglass, and concrete, each with their own advantages. Polyethylene tanks are lightweight, durable, and affordable, making them a popular choice. Fiberglass tanks are strong and corrosion-resistant, ideal for above-ground installations. Concrete tanks, while heavy and more expensive, provide excellent durability and insulation for underground storage.
To determine the appropriate size, calculate your roof’s yield based on its surface area and average rainfall. A general rule of thumb is to provide 20 liters of storage per square meter of roof area. However, the size will also depend on your intended use, such as irrigation, livestock watering, or domestic purposes. Larger tanks offer more flexibility during dry spells but require more space and investment.
Consider the tank’s location, ensuring it is easily accessible for maintenance and close to the areas where the water will be used. Elevating the tank can improve water pressure for gravity-fed systems. Lastly, make sure to choose a tank with a tight-fitting cover to prevent evaporation, contamination, and mosquito breeding. With careful consideration of these factors, you can select the optimal storage solution for your rainwater harvesting system.

Maintaining and Using Harvested Rainwater
Water Quality and Treatment
Ensuring the quality of harvested rainwater is essential for its safe use in agricultural applications. A simple filtration system can be set up using a series of screens and filters to remove debris, leaves, and sediment. Begin with a coarse screen to catch larger particles, followed by progressively finer screens or mesh filters. A final stage of filtration using sand, activated carbon, or ceramic filters can help remove smaller contaminants and improve water clarity.
To treat the filtered rainwater, consider using UV light sterilization or chlorination to eliminate harmful bacteria and pathogens. UV light systems expose the water to ultraviolet radiation, effectively neutralizing microorganisms without adding chemicals. Chlorination involves adding small amounts of chlorine to the water, which disinfects it and prevents bacterial growth. It’s crucial to monitor and maintain the correct chlorine levels to ensure the water remains safe for crops and livestock.
Regular testing of the harvested and treated rainwater is recommended to verify its suitability for agricultural use. Simple water quality test kits can be used to check for pH levels, dissolved solids, and the presence of contaminants. By implementing these filtration and treatment methods, Canadian farmers can confidently utilize harvested rainwater to support their crops and animals while promoting sustainable practices on their farms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, harvesting rainwater from your roof is a simple, yet effective way to support sustainable agriculture practices in Canada, particularly in the Alberta region. By implementing a rainwater harvesting system, you can reduce your reliance on municipal water supplies, lower your water bills, and minimize your environmental impact. With proper setup, maintenance, and usage, you can ensure a reliable source of water for your crops, livestock, and other agricultural needs.
We encourage all Canadian farmers and individuals interested in sustainable agriculture to start harvesting rainwater from their roofs. By doing so, you not only benefit your own farming operations but also contribute to the collective effort of conserving water resources and promoting eco-friendly practices in our communities.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. The Organic Farming, The Canadian Way platform is here to support you with additional resources, workshops, and a network of like-minded individuals who share your passion for sustainable agriculture. Together, we can make a positive impact on our environment and ensure a thriving future for Canadian agriculture.
Start your rainwater harvesting journey today and join the growing community of Canadian farmers who are embracing sustainable practices. Let’s work together to create a more resilient and environmentally conscious agricultural landscape in Canada.











